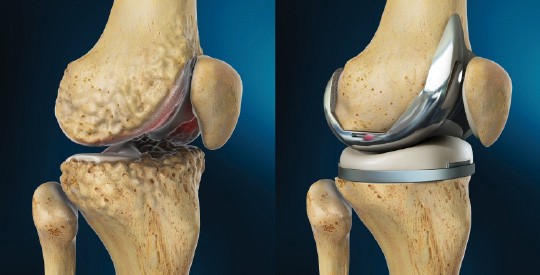
Joint Replacement Surgery
Replacement arthroplasty, or joint replacement surgery, is a procedure of orthopedic surgery in which an arthritic or dysfunctional joint surface is replaced with an orthopedic prosthesis. Joint replacement is considered as a treatment when severe joint pain or dysfunction is not alleviated by less-invasive therapies.
Technique
Before major surgery is performed, a complete pre-anaesthetic work-up is required. In elderly people this usually would include ECG, urine tests, hematology and blood tests. Cross match of blood is routine also, as a high percentage of people receive a blood transfusion. Pre-operative planning requires accurate Xrays of the affected joint, implant design selecting and size-matching to the xray images (a process known as templating).
A few days' hospitalization is followed by several weeks of protected function, healing and rehabilitation. This may then be followed by several months of slow improvement in strength and endurance.
Early mobilisation of the person is thought to be the key to reducing the chances of complications[1] such as venous thromboembolism and Pneumonia. Modern practice is to mobilize people as soon as possible and ambulate with walking aids when tolerated. Depending on the joint involved and the pre-op status of the person, the time of hospitalization varies from 1 day to 2 weeks, with the average being 4–7 days in most regions.
Physiotherapy is used extensively to help people recover function after joint replacement surgery. A graded exercise programme is needed initially, as the person's muscles take time to heal after the surgery; exercises for range of motion of the joints and ambulation should not be strenuous. Later when the muscles have healed, the aim of exercise expands to include strengthening and recovery of function.
